Assignment: Sensing: Potentiometers
Collaborators:
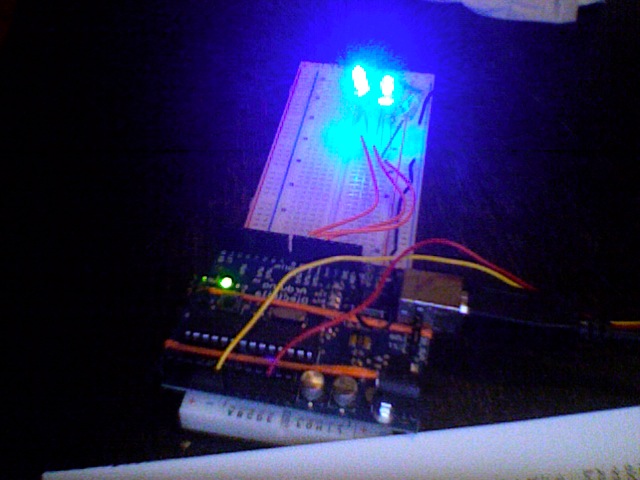
With a diffuser around three LEDs, we can easily make any color of the rainbow. The purpose of this project is to control that input, so that by turning a knob, the user can choose from any of the colors in the rainbow.
This only requires one potentiometer -- we can take the rotation of the pot to be the hue and use a nifty algorithm to convert hue into RGB tuples.
/*
* npdoty hue_rotation
* (now with blinking!)
*
* started with:
* one pot fades one led
* modified version of AnalogInput
* by DojoDave <http://www.0j0.org>
* http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/AnalogInput
*/
int potPin = 0; // select the input pin for the potentiometer
int potBlinkPin = 1; //the input pin for the second potentiometer
int ledPin = 11; // select the pin for the LED
int val = 0; // variable to store the value coming from the sensor
int blink = 0;
int i = 0;
float h_k = 0.0;
float angles[3];
int pins[3];
float values[3];
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
//these are the three PWM output pins I'm using
pins[0] = 11;
pins[1] = 10;
pins[2] = 9;
}
void loop() {
val = analogRead(potPin); // read the value from the sensor, between 0 - 1024
blink = analogRead(potBlinkPin);
h_k = (float)val / (float)1024; //calculate the fractional hue value
hueToRgb(h_k);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i ++)
{
analogWrite(pins[i], values[i] * 255);
}
delay(blink);
for (i = 0; i < 3; i ++)
{
analogWrite(pins[i], 0);
}
delay(blink);
}
void printFloat(float num)
{
Serial.print((long)(num*1000));
}
//takes a hue value between 0 and 1 and fills the values[] array with the rgb equivalents
//for more, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSL_color_space
//assumes that Lightness is 0.5 and saturation is 1.0
void hueToRgb(float hue)
{
angles[0] = hue + (1.0/3.0);
angles[1] = hue;
angles[2] = hue - (1.0/3.0);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
if (angles[i] < 0)
{
angles[i] ++;
} else if (angles[i] > 1)
{
angles[i] --;
}
float value = 0;
Serial.print(" Angle: ");
printFloat(angles[i]);
if (angles[i] < (1.0/6.0))
{
value = angles[i] * 6;
}
else if (angles[i] < (1.0/2.0))
{
value = 1.0;
}
else if (angles[i] < (2.0/3.0))
{
value = 6 * ((2.0/3.0) - angles[i]);
}
else
{
value = 0.0;
}
values[i] = value;
Serial.print(" Value: ");
printFloat(values[i]);
}
Serial.println("");
}
And just to prove that it can be done, here's a blinking, rotating rainbow.