Description
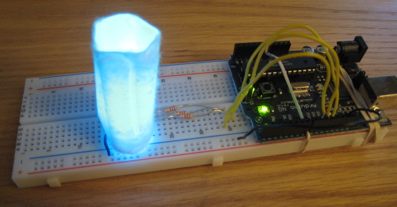
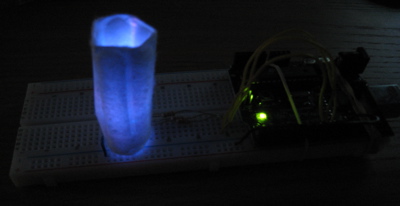
For a diffuser, I used a cotton swab taped along the long edge into a cylinder.
For the first set of code, I modified the Enhanced LED code so that each time, 'r', 'g', and 'b' are pressed, brightness in the corresponding LED increases by 10%. I also modified the code so that, each time an input is read, the LED levels reset and start over.
For example, input 'rrrggb' will set the red LED to 30%, green to 20%, and blue to 10%. The next time an input is read (for example, 'ggrr'), the LED brightnesses will be reset to 0 and then set to the new input level (in this example, green at 20%, red at 20%, and blue at 0%).
If a user types in more than 100% of any LED color (for example, types 'g' 11 times or 20 times), the LED of that corresponding color will default to the maximum (100%).
For the second set of code, I modified the Enhanced LED code so that the user can input a sequence they would like the LEDs to flash. So, if a user inputs 'rgbggbgbb', the LED would flash in the sequence red, green, blue, green, green, blue, green, blue, blue. The LEDs illuminate for .5 seconds each time and then turn off. A link to a sample video is included.
Components Used
Arduino Microprocsessor
Breadboard
3 220 Ohm Resistors
Red, green, blue LEDs
Cotton Swab taped into cylinder for diffuser
Arduino Code 1 - %
/*
* Serial RGB LED
* ---------------
* Serial commands control the brightness of R,G,B LEDs
* Command structure is "<colorCode>*", where "colorCode" is
* one of "r","g", or "b".
* E.g. "r" sets the red LED brightness to 10%
* "rrr" sets the red LED brightness to 30%
* "ggb" sets the green LED brightness to 20& and the blue by 10%
*
* Each time an input is read, the LEDs reset
*
* Created 18 October 2006
* copyleft 2006 Tod E. Kurt <tod@todbot.com
* http://todbot.com/
*
* Adapted 5 September 2007
* copylefter 2007 Ryan Aipperspach <ryanaip@alumni.rice.edu>
*
* Adapted 13 September 2007
* copylefter 2007 Jonathan Breitbart <breity@berkeley.edu>
*
*/
//include support for manipulating strings.
//for a useful string comparison function, see the bottom of this file... stringsEqual()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char serInString[100]; // array that will hold the different bytes of the string. 100=100characters;
// -> you must state how long the array will be else it won't work properly
char colorCode;
int colorVal;
int redPin = 9; // Red LED, connected to digital pin 9
int greenPin = 10; // Green LED, connected to digital pin 10
int bluePin = 11; // Blue LED, connected to digital pin 11
int redValue = 127;
int greenValue = 127;
int blueValue = 127;
float redValueFloat = 0;
float greenValueFloat = 0;
float blueValueFloat = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT); // sets the pins as output
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
analogWrite(redPin, redValue); // set them all to mid brightness
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue); // set them all to mid brightness
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue); // set them all to mid brightness
Serial.println("enter color command (e.g. 'rrrrrrrrbbbb') :");
}
void loop () {
//read the serial port and create a string out of what you read
readSerialString(serInString, 100);
//reset each float value
//so that each LED resets to 0 each time there is an input
blueValueFloat = 0;
redValueFloat = 0;
greenValueFloat = 0;
//read commands of the form 'rrrb'
processRepeatKeyCommands(serInString, 100);
//Erase anything left in the serial string, preparing it for the
//next loop
resetSerialString(serInString, 100);
delay(100); // wait a bit, for serial data
}
void resetSerialString (char *strArray, int length) {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
strArray[i] = '\0';
}
}
//read a string from the serial and store it in an array
//you must supply the array variable
void readSerialString (char *strArray, int maxLength) {
int i = 0;
if(!Serial.available()) {
return;
}
while (Serial.available() && i < maxLength) {
strArray[i] = Serial.read();
i++;
}
}
//go through the string, and increase the red value for each 'r',
//the green value for each 'g', and the blue value for each 'b'.
//For example "rrrg" sets red at 30% and green at 10%.
void processRepeatKeyCommands(char *strArray, int maxLength) {
int i = 0;
//loop through the string (strArray)
//i = the current position in the string
//Stop when either (a) i reaches the end of the string or
// (b) there is an empty character '\0' in the string
while (i < maxLength && strArray[i] != '\0') {
//Read in the character at position i in the string
colorCode = serInString[i];
//If the character is r (red)...
if (colorCode == 'r') {
//Increase the current red value by 10%
redValueFloat = redValueFloat + 25.5;
//if user input more than 10 'r's, set red value to maximum
if (redValueFloat > 255) {
redValueFloat = 255;
}
redValue = (int)redValueFloat;
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
Serial.print("setting color r to ");
Serial.println(redValue);
//If the character is g (green)...
} else if (colorCode == 'g') {
//Increase the current green value by 10%
greenValueFloat = greenValueFloat + 25.5;
//if user input more than 10 'g's, set green value to maximum
if (greenValueFloat > 255) {
greenValueFloat = 255;
}
greenValue = (int)greenValueFloat;
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
Serial.print("setting color g to ");
Serial.println(greenValue);
//If the character is b (blue)...
//Increase the current blue value by 10%
} else if (colorCode == 'b') {
blueValueFloat = blueValueFloat + 25.5;
//if user input more than 10 'b's, set blue value to maximum
if (blueValueFloat > 255) {
blueValueFloat = 255;
}
blueValue = (int)blueValueFloat;
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
Serial.print("setting color b to ");
Serial.println(blueValue);
}
//in case any of the colors have not been used in the input
//set those values to default (0)
blueValue = (int)blueValueFloat;
greenValue = (int)greenValueFloat;
redValue = (int)redValueFloat;
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
//Move on to the next character in the string
//From here, the code continues executing from the "while" line above...
i++;
}
}
//compare two strings to see if they are equal
//compares the first 'numCharacters' characters of string1 and string2 to
//see if they are the same
//
//E.g. stringsEqual("hello","hello",5) => true
// stringsEqual("hello","helaabbnn",3) => true
// stringsEqual("hello","helaa",5) => false
boolean stringsEqual(char *string1, char *string2, int numCharacters) {
if (strncmp(string1, string2, numCharacters) == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
Arduino Code 2 - Sequence
/*
* Serial RGB LED
* ---------------
* Serial commands control a sequence of R,G,B LEDs
* Command structure is "<colorCode>*", where "colorCode" is
* one of "r","g", or "b".
* E.g. "r" sets the red LED brightness to 100% for .5 seconds
* "rrr" sets the red LED brightness to 100% for .5 seconds three times in a row
* "ggb" sets the green LED brightness to 100% for .5 seconds twice and the blue to 100% for .5 seconds once
*
* The LEDs reset to 0 after they have been illuminated each time.
*
* Created 18 October 2006
* copyleft 2006 Tod E. Kurt <tod@todbot.com
* http://todbot.com/
*
* Adapted 5 September 2007
* copylefter 2007 Ryan Aipperspach <ryanaip@alumni.rice.edu>
*
* Adapted 13 September 2007
* copylefter 2007 Jonathan Breitbart <breity@berkeley.edu>
*
*/
//include support for manipulating strings.
//for a useful string comparison function, see the bottom of this file... stringsEqual()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char serInString[100]; // array that will hold the different bytes of the string. 100=100characters;
// -> you must state how long the array will be else it won't work properly
char colorCode;
int colorVal;
int redPin = 9; // Red LED, connected to digital pin 9
int greenPin = 10; // Green LED, connected to digital pin 10
int bluePin = 11; // Blue LED, connected to digital pin 11
int redValue = 0;
int greenValue = 0;
int blueValue = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT); // sets the pins as output
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
analogWrite(redPin, redValue); // set them all to mid brightness
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue); // set them all to mid brightness
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue); // set them all to mid brightness
Serial.println("enter color sequence (e.g. 'rrbgbbrbg') :");
}
void loop () {
//read the serial port and create a string out of what you read
readSerialString(serInString, 100);
//read commands of the form 'rrrb'
processRepeatKeyCommands(serInString, 100);
//Erase anything left in the serial string, preparing it for the
//next loop
resetSerialString(serInString, 100);
delay(100); // wait a bit, for serial data
}
void resetSerialString (char *strArray, int length) {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
strArray[i] = '\0';
}
}
//read a string from the serial and store it in an array
//you must supply the array variable
void readSerialString (char *strArray, int maxLength) {
int i = 0;
if(!Serial.available()) {
return;
}
while (Serial.available() && i < maxLength) {
strArray[i] = Serial.read();
i++;
}
}
//go through the string, and increase the red value for each 'r',
//the green value for each 'g', and the blue value for each 'b'.
//For example "rrrg" sets red at 30% and green at 10%.
void processRepeatKeyCommands(char *strArray, int maxLength) {
int i = 0;
//loop through the string (strArray)
//i = the current position in the string
//Stop when either (a) i reaches the end of the string or
// (b) there is an empty character '\0' in the string
while (i < maxLength && strArray[i] != '\0') {
//Read in the character at position i in the string
colorCode = serInString[i];
//If the character is r (red)...
if (colorCode == 'r') {
//set red LED to 100%
redValue = 255;
analogWrite(redPin, redValue);
Serial.println("setting color to red");
//keep LED lit for .5 second
delay(500);
//turn red LED off
analogWrite(redPin, 0);
//wait .1 seconds
delay(100);
//If the character is g (green)...
} else if (colorCode == 'g') {
//set green LED to 100%
greenValue = 255;
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue);
Serial.println("setting color to green");
//keep LED lit for .5 second
delay(500);
//turn green LED off
analogWrite(greenPin, 0);
//wait .1 seconds
delay(100);
//If the character is b (blue)...
//Increase the current blue value by 10%
} else if (colorCode == 'b') {
//set blue LED to 100%
blueValue = 255;
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue);
Serial.println("setting color to blue");
//keep LED lit for .5 seconds
delay(500);
//turn blue LED off
analogWrite(bluePin, 0);
//wait .1 seconds
delay(100);
}
//Move on to the next character in the string
//From here, the code continues executing from the "while" line above...
i++;
}
}
//compare two strings to see if they are equal
//compares the first 'numCharacters' characters of string1 and string2 to
//see if they are the same
//
//E.g. stringsEqual("hello","hello",5) => true
// stringsEqual("hello","helaabbnn",3) => true
// stringsEqual("hello","helaa",5) => false
boolean stringsEqual(char *string1, char *string2, int numCharacters) {
if (strncmp(string1, string2, numCharacters) == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
<a href="http://tels.berkeley.edu/~breity/LED_sequence2.mov">Link to sample video.</a>