|
Home Announcements Schedule Assignments |
IS250 Computer Based Communications Networks and Systems Spring
2010 |
Assignment 5 Solutions
Assignment 5 is due at 2pm (before start of
class) on Tuesday 4/13. Please see grading
policy on course
homepage for additional details regarding early/late submissions.
Please submit your answers in plain text (with any images as
attachments) to i250hw@ischool.berkeley.edu.
1. Shortest Path Routing
(a) (3 points) Using Dijkstra's Shortest Path First algorithm,
find the
shortest-path
routes from node C to all other nodes in the network. Show the
intermediate
results after each iteration step of the algorithm.
(b) (1 point) What is the final
routing
table for node C?
Note: answers for intermediate steps may vary slightly if next closest node is a tie, but the final answer should be the same.
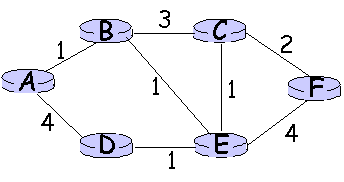
(a) Solution using Dijkstra's Shortest Path First algorithm:
Note: answers for intermediate steps may vary slightly if next closest node is a tie, e.g., CEB instead of CEF, but the final answer should be the same.
| Step | Start N | D(A),p(A) | D(B),p(B) | D(D),p(D) | D(E),p(E) | D(F),p(F) |
| 0 | C |
infinity |
3,C | infinity | 1,C | 2,C |
| 1 | CE | infinity | 2,E | 2,E | 1,C | 2,C |
| 2 | CEF | infinity |
2,E |
2,E |
1,C |
2,C |
| 3 | CEFD | 6,D |
2,E | 2,E | 1,C |
2,C |
| 4 | CEFDB | 3,B |
2,E |
2,E |
1,C |
2,C |
| 5 | CEFDBA | 3,B |
2,E |
2,E |
1,C |
2,C |
(b) What is the final routing table for node C?
Routing Table (Node C)
| Destination | Link to use | Cost |
| A | E | 3 |
| B | E | 2 |
| D | E |
2 |
| E | E | 1 |
| F | F |
2 |
2. Policy Based Routing
In addition, there are four stub ASs, AS44, AS55, AS66, and AS77. AS44 is a customer of AS1. AS55 is a customer of AS2. AS66 is a customer of AS3. Finally, AS77 is a customer of both AS1 and AS3.
(a) (2 points) Following the notation in slides 24-25 of the lecture on routing, draw a graph representing the internetwork and the relationships between the seven AS's.

(b) (1 point) A host in AS44 wishes to send a message to a host in AS66. Identify all possible AS-level paths that may be taken by the message.
There is only one possible path: AS44-AS1-AS2-AS3-AS66
(c) (1 point) A host in AS55 wishes to send a message to a host in AS77. Identify all possible AS-level paths that may be taken by the message.
There are two possible AS-level paths: AS55-AS2-AS1-AS77 and AS55-AS2-AS3-AS77.
(d) (1 point) If there are multiple AS-level paths to a given destination, how is the actual packet forwarding path selected?
Path selection may be based on a number of different factors, including routing policies as encoded in values of BGP attributes (e.g., weight, local preference, MED), the comparison of AS path lengths, etc.
(e) (1 point) Explain why the presence of a path at the physical layer or data link layer does not imply the presence of an AS-level path at the network layer.
AS-level forwarding paths are established not by physical connectivity, but through the advertisements of routes. For example, AS1 and AS3 may have a physical connection through the multihomed stub AS77. However, as a stub AS, AS77 will not forward a route advertisement from AS1 to AS3, nor a route advertisement from AS3 to AS1. As a result, neither the path AS1-AS77-AS3 nor the path AS3-AS77-AS1 exist. Put another way, stub ASs will never serve as transit network for traffic that neither originate nor terminate within its own network, even if it is multihomed.
3. TCP Reliable Data Transport
Host A and Host B are communicating over a TCP connection.
Host B has already received from Host A all bytes up to and including
byte 5000.
Next, Host A sends two more segments to Host B. The first segment
contains 100 bytes of data, has a sequence number of 5001, with source
and destination port numbers of 6200 and 7300 respectively. The second
segment contains 200 bytes of data.
Host B sends an acknowledgement whenever it receives a segment from
Host A.
(a) (1 point) What are the values for the sequence number, source port,
and
destination port for the second segment?
SEQ: 5101
SRC: 6200
DES: 7300
(b) (1 point) If the first segment has just arrived, and the
second
segment has
not yet arrived, what values should Host B use for the acknowledgement
number, source port, and destination port when constructing the
acknowledgment message?
ACK: 5101
SRC: 7300
DES: 6200
(c) (1 point) If the second segment arrives first, and the
first segment
has not
yet arrived, what values should Host B use for the acknowledgement
number, source port, and destination port when constructing the
acknowledgment message?
ACK: 5001
SRC: 7300
DES: 6200
(d) (3 points) Suppose that the first segment arrives,
followed by the second
segment. The first acknowledgment is lost, and the second
acknowledgment arrives at Host A after the first timeout period. Draw a
timing diagram, showing these messages and all subsequent segments and
acknowledgements sent, assuming that no additional messages are lost.
For each message, provide the sequence number or the acknowledgement
number, where appropriate.

4. UDP and Addressing
(2 points) A process running on Host A has a UDP socket with
port number
20000. Suppose both Host B and Host C both send a UDP datagram to Host
A with destination port number 20000. Will both datagrams be delivered
to the same process on Host A? If so, how will the process at Host A
know that the two datagrams orginated from two different hosts?
Yes, both datagrams will be delivered to the same process
on Host A. Host A will know that the two messages originated from two
different hosts because they have different source IP addresses.